Table of Contents
Definition of Elrond
Elrond is the distributed transactional computation protocol that relies on a sharded state architecture and a secure Proof of Stake consensus mechanism.
What is Elrond?
A blockchain platform with sharding architecture is called Elrond. It uses the consensus algorithm known as Secure Proof-of-Stake or SPoS. How does it operate? Is it truly necessary? Let’s investigate together!
Depending on the workload, the Elrond blockchain can be split up into multiple segments, or shards. Every shard is a separate network that requires a different set of validators to function.
For shard interaction, every block is broken into three sections. It is also possible to divide up a transaction and confirm it concurrently on several shards. Network segment synchronization happens in phases, and then components from every chain are combined to form the so-called meta blockchain.
In July 2020, the primary Elrond network went live, claiming a maximum throughput of 263,000 transactions per second.

How Does Elrond Work?
The network is split up into pieces known as shards, each of which has a unique set of validators, to execute transactions. Three categories apply to Elrond’s fragmentation: states, transaction groups, and networks.
The practice of organizing groups of validators to reach a consensus is known as sharding. By dividing transaction groups among validator committees, they become fragmented. State sharding is the process of processing and storing some of the transaction results by individual network fragments. Segment synchronization is required for transaction completion and must be done regularly.
Adaptive sharding is used on the Elrond blockchain. The network is divided into fragments, the number of which varies depending on the current load. This adaptability guarantees high performance and safety.
Sharding also involves embedding network segments into binary tree nodes without descendants. At first, all nodes are divided into two groups. The network is divided into four, six, or more fragments if necessary.
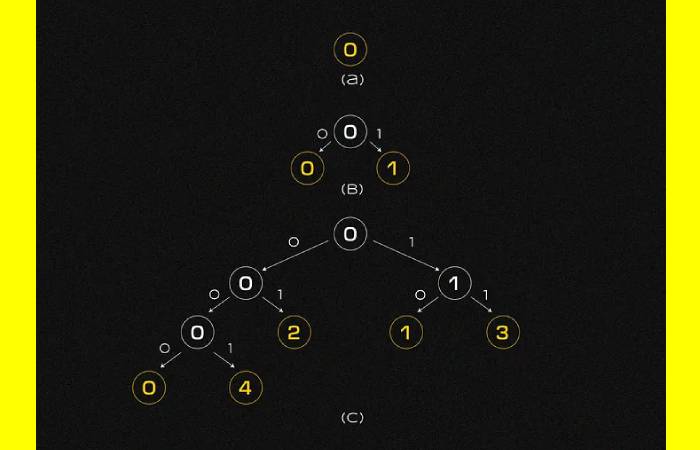
Why is it Different from other Blockchains?
- Though most other blockchain networks require custom hardware and high energy consumption, Elrond runs on average computers.
- By employing sharding, a method of parallelizing data & transaction processing, Elrond’s performance scales up with the number of computers joining the network.
- And we are reaching more than 100.000 transactions per second while growing increasingly decentralized.
- Also, the Elrond network is the first to present a viable solution.
- And where all the three aspects of sharding – state, web, and transactions. Also are implemented at once.
- Also, combined with its “Adaptive” component, its novel architecture allows for dynamic network configuration to maintain a high level of security through scaling with demand.
- In addition to scaling through sharding, Elrond also approaches the consensus problem with the mechanism called Secure Proof of Stake.
- Which mitigates potential attack vectors compared to Proof of Work while also enabling large throughput and fast execution.
- By solving some of the most brutal consensus and sharding problems in the blockchain space, Elrond can provide very high performance on a network made of inexpensive computers.
- And they are also resulting in a meager cost per transaction.
- in addition to the performance and price.
- Elrond also stands out through the quality of the developer experience and the resulting boost in usability on the end-user side.

